Which Best Describes a Nerve Impulse
Hence Dendrite cell body axon is the pathway that a nerve impulse travels through a neuron. The motor nerve generates an impulse to transfer signals from neurons to neuromuscular junction.

Nerve Impulse Its Transmission Impulse Generation Videos Examples
In neurons with myelin sheaths ions flow across the membrane only.

. In medullated nerve fibres white fibres the impulse jumps from node to node it is called saltatory propagation Fig. Chemical transmission through neutrons and chemical. A nerve impulse has caused some muscle action to be produced.
The speed of transmission of nerve impulse also depends upon the diameter of the fibre. Sensory neuron interneuron motor neuron. These messages are nerve impulses and each message is a quick electrical impulse.
Nerve impulse that a nerve impulse travels through a neuron is from the dendrites then to the cell body then to the axon. The muscular system is made up of about 150 muscles. Depolarization and generation of action potential.
These long thread-like pieces are where nerve impulses are transmitted. The muscular system helps in digestion and circulation. This stimulates sarcoplasmic reticulum to release calcium into the muscle cells.
A stimulus which is above the threshold level is applied to a receptor. The resting membrane potential changes from 70 mV to 30 mV. Interneuron sensory neuron motor neuron.
Calcium in the muscle cells binds with troponin causes actin and myosin to bind. The muscular system allows conduction of nerve impulses. A flow of neurotransmitters through a nerve 4.
The potassium gates in the cell membrane open and potassium ions fl ood. A tiny gap separating one neuron from another through which messages are carried. Sensory neuron motor neuron interneuron.
The correct order of transmission of nerve impulses along the visual pathway is. None of the above. An action potential is due to the movement of ions in and out of the cell.
Chemical signals move the impulses within the. A moving temporary depolarization of the axon membrane 3. A nerve impulse is a sudden reversal of the electrical charge across the membrane of a resting neuron.
The nerve impulse is transmitted by the axon of one neuron to the dendrite of another and through dendrite to axon of another neuron through synapse. Electricity flowing through a neuron 2. It increases the speed of nerve impulse which is about 20 times faster in medulated than in non-medullated nerve fibres.
O 1 2 O 3 04. Motor neuron interneuron sensory neuron. Stimulus changes membrane permeability and sodium ions diffuse rapidly into the cell.
What statement best describes the resting state of a neuron. The optic II nerve terminates in which region of the brain. A nerve impulse is the electric signals that pass along the dendrites to generate a nerve impulse or an action potential.
Rootlike structures that receive neural impulses from other neurons. The tubelike part of a neuron that carries messages to other neurons. When a nerve impulse or action potential reaches the axon terminal synaptic transmission occurs via.
Which of the following correctly describes how nerve impulses move throughout the body. The nerve impulses are generated at the sensory receptors and are being brought to CNS by the sensory neurons. They are moved in and out of the cell through sodium and potassium channels and sodium-potassium pump.
Which best describes the pathwayorder of a nerve impulse passed between neurons in the correct order. Although the nervous system is very complex nervous tissue consists of just two basic types of nerve cells. Which best describes the muscular system.
Question 2 2 pts Which of the following best describes an action potential nerve impulse. Nerve impulse conduction refers to the propagation of nerve impulse that occurs due to a change in membrane potential beyond the cell membrane. The muscular system allows.
Each nerve has many extensions of individual nerve cells. Which one of the following is the correct sequence of events that correlates to the sequence of events of a nerve impulse. Neurons and glial cells.
Neurons are the structural and functional units of the nervous system. The reversal of charge is called an action potential. Which best describes the direction of the nerve impulse in cranial nerve II.
It specifically involves sodium and potassium ions. A type of nerve cell that has a specific function to deliver messages to the brain is called a neuron. Rod or cone bipolar cell ganglion cell.
An impulse travels along the neuron pathways as electrical charges move across each neural cell membrane. Nerve impulse refers to the generation of action membrane potential beyond the cell membrane in response to the stimulus. Electrical transmission through neurons and elecrical transmission between neurons.

Lesson Explainer Nerve Cells Nagwa

Lesson Explainer The Nerve Impulse Nagwa

Action Potential Versus Nerve Impulse A According To The Download Scientific Diagram

Oligodendrocyte Physiology Britannica
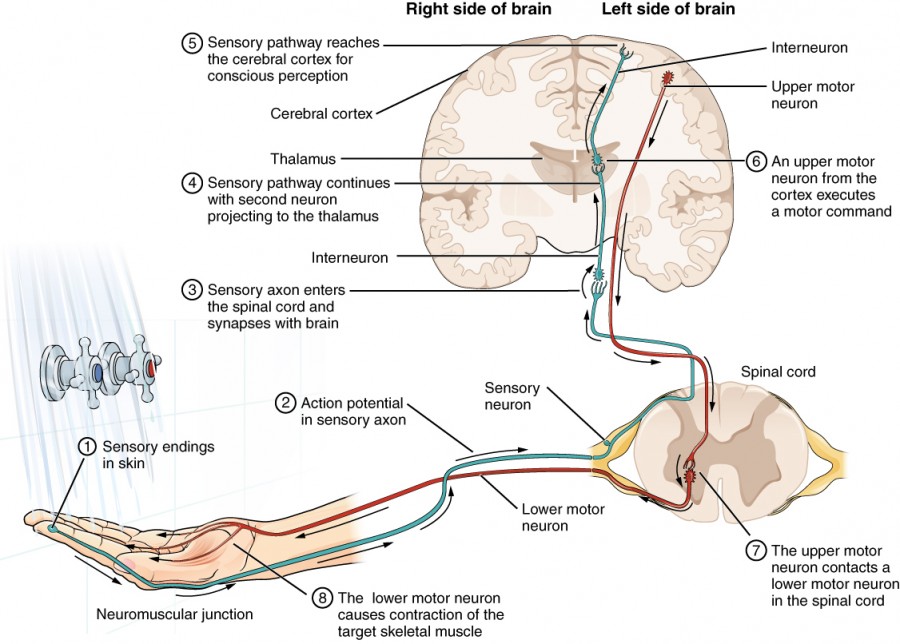
Impulse Conduction Anatomy And Physiology

Nerve Impulse Ck 12 Foundation
8 4 Nerve Impulses Human Biology

Nerve Impulse Its Transmission Impulse Generation Videos Examples

Nervous System Receptors Sensor Motor Relay Neurones Synapses Effectors Reflex Arc Actions Five Sense Organs Ears Eyes Nose Skin Tongue Receptors Cells Sensitive To Stimulus Axon Dendrites Dendrons Igcse O Level Gcse 9 1 Biology
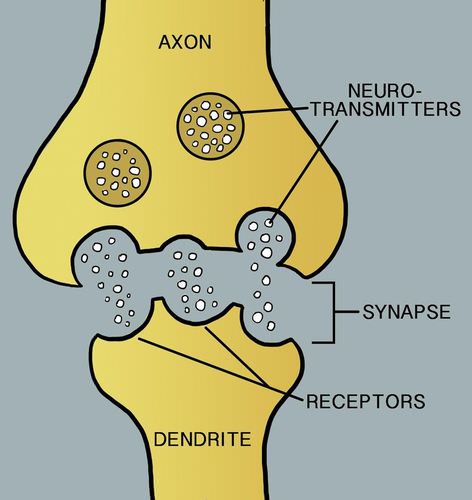
Nerve Impulse Ck 12 Foundation

Nerve Impulse Ck 12 Foundation

Lesson Explainer The Nerve Impulse Nagwa

Nerve Impulse Ck 12 Foundation

Nervous System Receptors Sensor Motor Relay Neurones Synapses Effectors Reflex Arc Actions Five Sense Organs Ears Eyes Nose Skin Tongue Receptors Cells Sensitive To Stimulus Axon Dendrites Dendrons Igcse O Level Gcse 9 1 Biology
Why Do Non Myelinated Nerve Fibres Even Exist As Myelinated Ones Can Actually Conduct Impulses Faster Quora


Comments
Post a Comment